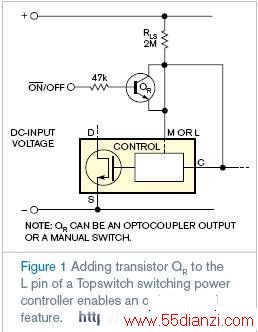
图1 连接在M或L引脚和控制引脚之间的NPN型晶体管QR
图2中的电路提供一个新功能,允许使用有时比控制引脚更方便的 接地开关 ,控制稳压器开关。在机械开关的情况下,电路不需要外部电源实现这个功能。这个功能应用尤为重要,Topswitch的电源供给是唯一电源。电路不会干扰M或L引脚的过电压和欠电压功能。为理解图2中电路的功能需要M或L引脚内部工作原理的解释。这个引脚起到接近2V直流的恒值电压源作用,并使RLS提供的外部电路电流降低。过电压和欠电压检测的内部电流敏感极限大概50 &mICro;A,伴有30 µA的欠电压,和225 µA的过电压滞后。这就是说,当流入M或L引脚的电流少于30 µA或在30~50 µA之间时,稳压器输出由于欠电压而关闭。当流入M或L引脚的电流为225 µA的时候,稳压器输出由于过电压而关闭。当流入M或L引脚的电流为50到225 µA的时候,输出被使能。

图2 为Topswitch芯片的开关控制添加接地开关的功能电路
图2中电路按如下方式工作:当Q1集电极负载的开关导通时,Q1作为简单二极管使射极到
基极产生0.6V压降。所有RLS提供的电流通过Q1的基-射极结点和150kΩ电阻进入M或L引脚。在这种模式下,Topswitch集成电路敏感过电压和欠电压的极限。然而,当开关接地时,Q1的功能就相当于有高增益的饱和晶体管。这个电路吸收大部分由RLS到地的电流作为Q1的集电极电流。Q1的小基极电流加上4 µA,通过150kΩ电阻流入M或L引脚。对图2中数值,甚至在Q1具有最小增益和最大450V输入电压的时候,基极电流也小于3.8µA。因此,3.8µA或7.8µA流入M或L引脚。这种低电流进入 “fools”引脚和稳压器的“thinking”,输入电压处于欠电压状态,而使稳压器输出关闭。
如果另外有个电压或电流源存在,用仅有减小电流作用的集电极开路开关代替S1。如果遥控开关驱动像逻辑门输出一样,产生或消除电流,应该在Q1的集电极负载处插入二极管,驱动器必须驱动二极管阴极高于直流2V来关闭稳压器(图2可选)。M引脚也允许电流极限的调节。
英文原文:
Add a grounded-switch feature for Topswitch on/off control
Adding a couple of components to the control PIN of a Topswitch switching regulator enables on/off control.
Robert N Buono, Aeolian Audio LLC, BloomfiELD, NJ; Edited by Charles H Small and Fran Granville -- EDN, 6/21/2007
The Power Integrations Topswitch family of integrated flyback-regulator ICs provides exceptional performance in small, low-pin-count PACkages. For the lowest-pin-count packages, the multifunction, or M, pin serves multiple purposes, including on/off control and undervoltage- and overvoltage-input detection. Other package types include an L pin, which also provides this function. The application notes and data sheets show how to implement the various features available at these pins. For example, to allow remote on/off control and still preserve undervoltage and overvoltage functions, the application drawings show an NPN transistor, QR, which connects between the M or L pin and the Control pin (Figure 1). To turn off the regulator, QR must be biased on. To achieve this goal requires a base voltage of 2.6V dc or greater.
The circuit in Figure 2 provides a new feature that allows you to switch the regulator on or off usi ng a grounded switch that is sometimes more convenient to implement than a switch that references to the Control PIN. In the case of a mechanICal switch, this circuit would require no external power to implement this function. This feature is important in applications in which the Topswitch power supply is the only source of power. This circuit does not disturb the functioning of the undervoltage and overvoltage functions of the M or L pin. To understand the functioning of the circuit in Figure 2 requires an explanation of the internal workings of the M or L pin. This pin acts as a constant voltage source at approximately 2V dc and sinks current from the external circuit, which RLS supplies. The internal current-sense thresholds for undervoltage and overvoltage detection are roughly 50 µA with 30 µA of hysteresis for undervoltage and 225 µA for overvoltage. That is, when the current into the M or L pin is less than 20 µA, or 50–30 µA, the regulator output switches off because of undervoltage. When the current into the M or L pin exceeds 225 µA, the regulator output switches off because of overvoltage. When the current into the M or L pin is 50 to 225 µA, the output is enabLED.
The circuit of Figure 2 works as follows: When the switch in the collector lead of Q1 is open, Q1 functions as a simple diode with a 0.6V drop from EMItter to base. All the current that RLS supplies flows into the M or L pin through the base-emitter junction of Q1 and the 150-kΩ resistor. In this mode, the Topswitch IC senses the undervoltage and overvoltage thresholds. However, when the switch to ground closes, Q1 functions as a nonsaturated transistor with high gain. The circuit SIPhons off most of the current through RLS to ground as the collector current of Q1. Only a small base current from Q1 plus 4 µA through the 150-kΩ resistor flows into the M or L pin. For the values in Figure 2, this base current is less than 3.8 µA, even when Q1 has minimum gain and input voltage is at a maximum of 450V dc. Therefore, 3.8+4 µA, or 7.8 µA, flows into the M or L pin. This low current flowing into the pin “fools” the regulator into “thinking” that the input voltage is undervoltage, and the regulator output switches off.
If another voltage or current source is present, you could replace S1 with an open-collector switch that sinks current only. If the remote on/off driver CAN source and sink current, as the output of a logic gate can, then you should insert a diode in the collector lead of Q1, and the driver must drive the cathode of that diode above 2V dc to turn off the regulator (optional in Figure 2). The M pin also allows current-limit-threshold adjustment.
英文原文地址: http://www.edn.com/index.asp?layout=article&articleid=CA6451247&sPACedesc=DesignIdeas&taxid=10577&industryid=44217
本文关键字:开关 元器件特点及应用,元器件介绍 - 元器件特点及应用