4 性能测试结果
改进后的μC/OS-II已移植到ATmega128L开发板上,系统运行稳定。表2和表3分别为改进前和改进后在各种软件状态下测得的系统功耗。
表2 改进前的μC/OS-II在各种软件状态下的系统功耗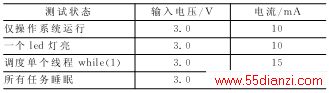
表3 改进后的μC/OS-II在各种软件状态下的系统功耗
5 结论
无线传感器网络节点作为一种嵌入式设备,很长时间都处于无任务运行的空闲状态。如果能够根据系统的工作状态自动进行功耗管理,使系统工作于与系统状态相适应的功耗模式,那么能够极大地降低系统功耗,从而延长系统的寿命。这在对能耗要求极高的无线传感器网络中有着重要意义。
参考文献
[1] Boulis A,Han C-C,Srivastava M B.Design and implementation of a framework for efficient and programmable sensor networks[C].In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Mobile Systems,Applications,and Services,2003:187-200.
[2] Jason Hill,et al.System Architecure Directions for Networed sensors[C].In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems,2000.
[3] Dunkels A,Gronvall B,Voigt T. Contiki-a lightweight and flexible operating system for tiny networked sensors.In Proceedings of the First IEEE Workshop on Embedded Networked Sensors,2004.
邱祎(硕士研究生),主要研究方向为嵌入式实时操作系统及其应用;
桑楠(教授),主要研究方向为高可信赖的实时操作系统、实时调度、分布式实时系统、普适计算及容错计算。
上一篇:配电网中性点接地方式分析